



































Original Cable Harness Manufacturer With 15+ Years of Experience




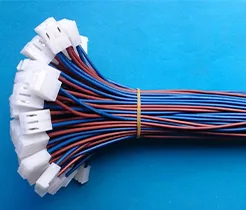































































































High temperature resistant wiring harness

Low temperature resistant wiring harness

Corrosion resistant wiring harness

5.5 2.1mm extension cable






































Customer's
Requirements
Engineer
Analyze

Send Quote

Sampling

Sampling

Drawing

Construct
Mass
Production

QC

Packing

Delivery

Customer's
Requirements

Engineer
Analyze

Send Quote

Sampling

Drawing

Construct

Mass
Production

QC

Packing

Delivery
Fast certification services: With 17 years of cable wire harness experience, Long-term cooperative testing laboratory can help get your certificates quickly.









An electrical or electronic system’s wiring harness is a collection of wires, cables, and connections that are connected to transfer power and signals between different parts of the system. It unifies several lines into a manageable entity, serving as the brains of numerous machines and devices. The wiring harness’s design makes installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting simpler by streamlining the intricate electrical connection. Wiring harnesses are an integral part of automotive, aircraft, consumer electronics, medical, and industrial equipment.
The main parts of the wiring harness, known as wires and cables, are in charge of carrying signals or current. Depending on the particular needs of various applications, different wire types will have varied insulation.
Connectors: Circuits are connected using connectors. They make and break connections between wire harnesses and other parts or systems. Ring terminals, blade connectors, and pin connectors are some of the connector types.
Terminal: A terminal is a piece of metal that has been soldered or crimped after the wire has been connected to the connection. They come in a variety of styles, including shovels, rings, sockets, pins, and so on. The connector type, current capacity, and environmental factors all influence the terminal choice.
Bushing or conduit: PVC, nylon, or high-temperature materials or chemicals can be used to make this protective coating for wrapping wires. It can add extra insulation, organize the wires better, and shield them from wear and tear.
Tie tape: Also referred to as a zipper, this nylon, metal, or other material tool is used to neatly wrap wires.
Marks or labels: Marks or labels are used to identify items, particularly intricate wire harnesses. Numerous label types exist, including sliding wire, printing sleeves, self-adhesive labels, and more.
Sealing ring: The wire harness passes through the opening in the panel or barrier using a sealing ring, which is made of rubber or plastic. They serve as a seal to keep out dust, moisture, and noise while shielding cables from jagged edges of holes.
Components for strain relief: Their purpose is to lessen the mechanical strain on electrical connections. Add a rubber sheath to protect the connector’s back or use a unique fixture to secure the wire harness close to the connecting site.
Shielding: The wiring harness may have metal shielding in applications where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is present. This can be foil wrapped around individual wires or a metal sleeve that has been braided.
A connector is a device that joins two or more wires in a harness. One can weld, crimp, or use special splice connectors.
Breakpoint: the point at which smaller groups inside the main harness are divided to reach separate locations. At these attachment places, the seat belts are typically strengthened to preserve their structural integrity.
Components that provide protection: These could include heat-shrinkable tubes that are used to shield joints or terminals from damage. Protective sleeve made of rubber or silica gel to attach environmental seal.
Fuses and circuit protection devices: Although not always part of the wiring harness itself, some designs include on-line fuses or circuit breakers to prevent over-current conditions.
Relay and module housing: In some complex wiring harnesses, especially in automotive applications, the wiring harness may include the housing of relays or electronic modules.
Automotive: Applications include advanced driver assistance systems, lighting, entertainment systems, electric windows, and engine management systems. More than 1000 separate wires and up to 100 wire harnesses can be found in modern autos.
Aerospace: It is crucial for spacecraft, satellites, helicopters, and airplanes. It is mostly utilized in the flight control system, navigation system, communication equipment, and cabin electronic equipment.
Consumer electronics: Included in home appliances, gaming consoles, PCs, and televisions. utilized for user interface connectivity, power distribution, and signal transmission between components.
Medical gadgets: they are crucial to the operation of imaging systems like CT and MRI scanners. utilized in surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, and patient monitoring systems. Industrial equipment: It is utilized in the production of robotics, machinery, and process control systems. Conveying systems, industrial sensors, and programmable logic controllers (PLC) are a few examples of applications. Usually, it’s required to be able to tolerate being around chemicals, very cold temperatures, or a lot of vibration.
Telecommunication: In data centers, network switches, and routers, it is crucial. utilized in satellite communication systems and equipment for cellular towers. Complex signal routing and the need for fast data transmission are typically involved.
Military vehicles: Utilized in communication devices, armament systems, and military vehicles for military and defense purposes. Radar systems, missile guidance, and battlefield communication devices are examples of applications.
Ships: Used in ships, submarines, and offshore oil drilling rigs, both marine and offshore. utilized in communication devices, propulsion control systems, and navigation systems.
Rail and mass transit: Applications include the passenger information display, signal system, and traction control. Generally speaking, compliance with the unique fire safety and durability requirements of public transportation is required.
Energy Sector: Applied to devices that generate electricity, such as solar and wind turbines. utilized in smart grid technology and power distribution systems. Usually, it’s essential to manage high voltage and endure harsh outside environments.
Agriculture: Applied to contemporary agricultural machinery, including harvesters, tractors, and irrigation systems. Applications include automatic control, output monitoring, and GPS navigation systems.
Heavy machinery: Used in heavy machinery including excavators, bulldozers, and drilling equipment in the mining and construction industries. utilized as a diagnostic interface, safety system, and equipment.
Rational vehicles and watercraft: Boats, private boats, RVs, and trailers are examples of rational vehicles and watercraft.
Robotics: Industrial robots, collaborative robots, and even humanoid robots require robotics. utilized for motor control, sensor connection, and power distribution.
Elevators and Escalators: Escalators and elevators are crucial for the user interface, security measures, and control system. must fulfill the unique safety requirements for equipment used in public spaces.
ATMs and vending machines: They are utilized for internal mechanisms, payment systems, and user interfaces. Usually made with simple component replacement and maintenance in mind.
HVAC systems: These include air conditioning, ventilation, and heating systems for both homes and businesses. utilized for sensor interface, motor connection, and thermostat control.
• Point-to-Point Harnesses: Connect two specific points.
• Breakout Harnesses: Feature a main trunk line with multiple branches.
• Custom Harnesses: Designed for specific applications with unique requirements.
• Modular Harnesses: Consist of separate modules that can be combined or replaced individually.
• Flat Ribbon Cable Harnesses: Use flat, flexible cables for space-constrained applications.
• Overmolded Harnesses: Encased in molded plastic for enhanced protection and durability.
The choice of harness type depends on factors like the complexity of the electrical system, space constraints, environmental conditions, and maintenance requirements
• Wire Harness: Consists of multiple individual wires bundled together, each serving different functions within a system.
• Cable Assembly: Typically refers to a single cable with multiple conductors within a shared outer jacket.
• Applications: Wire harnesses are used in complex systems like automobiles, while cable assemblies are used for straightforward connections like consumer electronics.
The choice between a wire harness and a cable assembly depends on factors such as the complexity of the electrical system, space constraints, flexibility needs, and specific application requirements. In many systems, both wire harnesses and cable assemblies may be used in different areas to optimize performance and functionality.
The main differences include:
• Electronic harnesses typically handle lower voltage and current levels.
• Electronic harnesses often involve more complex signal routing and shielding requirements.
• Electrical wiring harnesses generally focus on power distribution and may handle higher voltages and currents.
• Electronic harnesses may require more precise manufacturing tolerances and specialized connectors.
Several reasons are show below to explain the importance of wire harnesses. All can achieve enhanced performance, security and high-efficiency:
The simplicity of setup: Several wires are grouped by wire harnesses to a single and managable unit, which can simplify the setup processes since people who take are of the setup have smaller amount of loose wires to control. The routing and link processes are simplified, which allows the easy integration into the overall electrical system. This management is also helpful for decreasing the time and energy needed for setups, particularly in complicated systems with many connections.
Strengthened Safety: Greater protection is provided with a wire harness for the separated wires through the enclosure of them in a strong sheath. The protective layer prevents the wires from outdoor conditions like heat, humidity, vibrations, and so on. These conditions may cause damage to the wires and result in electrical malfunction or failed circuits. The proper insulation and sheath is helpful for avoiding electrical hazards, which the safe operation of the system can be allowed.
Intensified Durability: With the managable and protective construction, the wire harness enables the enhancement of a durable electrical system. Also, they has less possibilities to be exposed to wear and tear when grouped. And the harness can be built to endure the harsh weather factors. This durability helps extend the longevity for the electrical system.
Space-saving: Space plays a key role in many typical cases. Space can be conserved with the help of the wire harnesses through the grouping of several wires into a complete one, which allows the easy fit for narrow or limited places. The saved space plays a particularly essential role in applications like auto, aerospace, and electronic devices.
Fewer maintenance: With the nature of organization, a wire harness can enable the easier identification and tracking of the wires when in maintenance. This helps the significant reduction of time needed for inspecting and fixing electrical problems because of the neat grouping and labeling of the wires. In addition, damages may be less frequently occurred due to the protection against environmental conditions, which decrease the demands for fixes.
Cost reduction: Overall cost can be reduced due to the long-time advantages even the initial price of a wire harness may be higher. A more cost-effective way that helps extend the lifespan are created because the time for setup is reduced. Also, the maintenance needs are decreased and the durability is enhanced. Using wire harnesses is helpful for avoiding cost-increasing and electrical shorts that lead to damage.
Multiple steps are included in designing and producing wire harnesses. These steps guarantee that every harness fits the special needs of its required use. Careful planing, precise and cautious quality control are needed to create a stably functioned product. Detailed information is:
(1). Design
a. Requirements: Firstly, you need to learn about the detailed demands of the use when you get into the design part. Here detailed information about the electrical system where a wire harness is utilized should be collected. Additionally, electrical needs should be taken into consideration if you’re an engineer. The demands include current, voltage, wattage or even specific industrial safety standards that are required for the wire harness.
b. Schematic Design: A schematic diagram of the wire harness should be produced when the requirement is confirmed. The diagram contains detailed information of the wire routing, multiple element’s connections and the positioning of a connector, fuse, and relay. Also, serving as a template for the wire harness, the schematic plays a leading role in the design and production processes. The information of connector kinds and protective measures required are contained.
c. Prototype: A prototype of a wire harness may be produced Before the massive production. Applied to the testing of design and enable the functional requirements to meet, the prototype helps identify problems in the testing phase. And these issue can be fixed before the manufacturing commences. Also, you can adjust the design in this stage to achieve compatibility, easy and simple setup and good performance.
(2) Material:
The electrical needs and environmental factors determine the kinds of wires. Some commonly-use materials contain copper or aluminum for the conductors built with PVC or silicone insulation. The kind of connector is also important because it can help achieve safe and reliable links.
(3). Production:
Wire cutting is the first step for the production process. The wires need to cut to the exact lengths required in the design. Automated machines are often applied to enables the accuracy and consistency of several harnesses. At their ends where locates the attachment of connectors, the wiring harnesses are stripped of the insulation. Next, the exposed ends of the wires are equipped with right connectors, which is usually finished when crimping. Other elements like fuse and relay are also attached to the harness.
(4). Testing and Quality
After the assembly, the harness will undergo strict tests to make sure they meet the safety standards and quality certification. This include the continuous testing to verify the connections are well-functioned and resistant to harsh conditions. Also the insulation should be tested to check if they can ensure electrical risks
a. Application
the specific electrical needs should be assessed, which involves the voltage, current and signal types that the harness can carry. Also, it must have the capability to withstand high electrical load with no overheated issues or signal interference. The operation conditions should be considered. Aspects like extreme temperatures, sunlight or humidity-exposed, uv rays are included to make sure the harness can ensure the factors with no failure.
b. Connector Kinds
Compatibility is a key to the connectors to ensure the seamless connection between the wires and the systems. A incompatible connector may result in poor connection, enhanced resistance, or even other big electrical issue. In addition, connectors that are strong enough to ensure the harsh environments should be picked out. This involves the resistance to abrasion, corrosion and other harsh factors.
c. Current and Voltage
the wire harness must be able to withstand the max current needed bu the device with no excess ion of the required capacity. A overloaded harness may result in overheating, insulation loss and other electrical risks. What’s more, make sure the wire harness fits the required max voltage. If you use harness that cannot handle the voltage of the devices, insulation breakdown and other electrical risks may occur.
Several signs may be the reminders:
Firstly, if you encounter some intermittent electrical problems like flickering lights, it may be reminder for you to replace the harness because of the damage to the fog ligths.
Secondly, frayed wires or cracked insulation may be another sign to remind that you need to inspect the wires to avoid damage in the future.
Thirdly, if you find the connectors in loose conditions, you may need to replace it with a new one because it may result in overheated issue.
Yes, electrical tapes can be on a wiring harness. However, it can’t provide enough insulation by using cheap electrical tape or low-quality electrical tape. Also, put it in an environment exposed to high temperature, oil or other chemical material. What’s more, if you use them improperly, they will lead to a bad result.
High-quality electrical tape can offer a greater effect on insulation, such as dedicated tape in cars and electrical. Think about using heat shrink tubing, wire loom, or specialized wiring harness tape. Generally, they are more durable than standard electrical tape. Also, they can provide more extended protection.
Proper usage can delay the lifespan. You can wrap them tightly and around the wires equally. More lapping can ensure a great insulation effect. If the wire harnesses are exposed to a bad environment, it’s recommended to use specially designed materials.
Looking for Affordable Wiring Harnesses for Your Project?
As a renowned cable harness solution provider giant VOCSON can ensure that your project is leading the industry, Choose us to provide wire harness products, and OEM or ODM services for you.